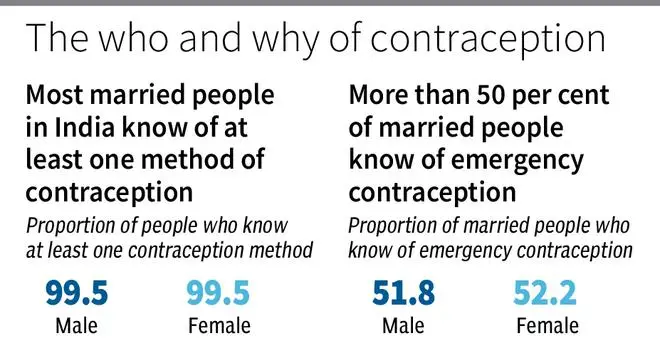
Most of the Indian population knows about contraceptive methods And more than 99 per cent of currently married women and men aged between 15-49 years know at least one method of contraception. More than half of currently married women (52%) and men (52%) know about emergency contraception.
Knowledge of contraception has gone up in the adolescent population. But despite these facts, more than one-third of men believe that contraception is women’s business, and 20 per cent of men believe that a woman who uses contraception may become promiscuous.
The latest National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5) brings out some interesting facts about family planning and the use of contraceptives.
Sterlisation popular
Female sterilisation remains the most popular modern contraceptive method. Among currently married women age 15-49, 38 per cent use female sterilisation, followed by male condoms (10%) and pills (5%). Ten percent use a traditional method, mostly the rhythm method. Among sexually active unmarried women, male condoms are the most commonly used method (27%), followed by female sterilisation (21%).
The report mentions that contraceptive prevalence rate among currently married women (age 15-49) increased from 54 per cent in 2015-16 to 67 percent in 2019-21. Among sexually active unmarried women (age 15-49), the use of condoms/Nirodhs increased from 12 per cent in 2015-16 to 27 per cent in 2019-21.
By employment status, 53 per cent of women who are not employed use a modern contraceptive method, compared with 66 per cent of women who are employed for cash. Modern contraceptive use increases with wealth, from 51 percent of women in the lowest wealth quintile to 59 per cent of women in the highest quintile.
State Scenario, Public Health Sector
Among the States, the use of contraceptive methods is the lowest in Meghalaya (27%), Mizoram (31%) and Bihar (56%), and highest in West Bengal, Odisha and Himachal Pradesh (74% each). Among the States, a relatively low proportion of currently married women uses contraceptive methods in all smaller states in the northeast region except for Sikkim and Tripura.
The report highlights the importance of the public health sector in family planning. Almost seven in 10 (68%) modern method contraceptive users obtained their method from the public health sector. The rest of the users of modern methods obtained their method from the private health sector, including NGOs or trust hospitals/clinics (25%) and other sources (7%), including shops, their husband, friends and relatives.
More than eight in 10 (81%) women who got sterilised underwent the procedure in a public health sector facility, mostly a government/municipal hospital or a CHC/rural hospital/Block PHC.
The public health sector is the major source of female and male sterilisation, IUDs/PPIUDs and injectables, whereas the private health sector is the major source of pills, injectables and condoms/Nirodhs. Nearly half (45%) the pill users got their supply from the private health sector, and 41 percent from the public health sector.

‘It’s women’s business’
More than one-third of men believe that contraception is women’s business and that men should not have to worry about it, states the NFHS-5 report.
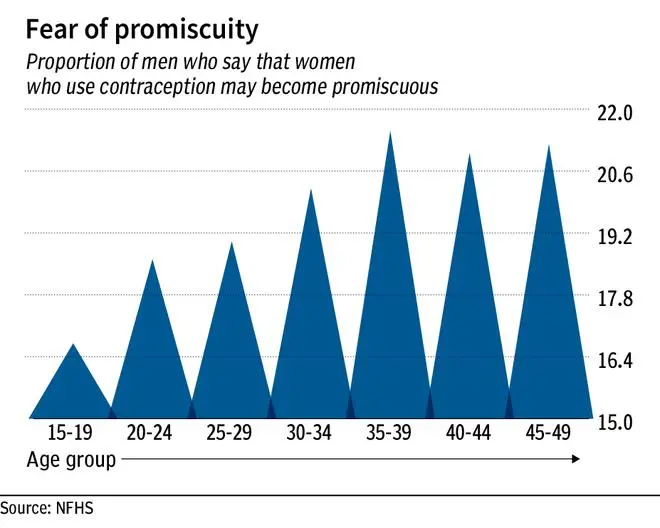
Twenty percent of men believe that a woman who uses contraception may become promiscuous. More than half (55%) of men reported that if a male condom is used correctly, it protects against pregnancy ‘most of the time’. An additional one-third of men said that a condom ‘sometimes’ protects against pregnancy if it is used correctly.








Comments
Comments have to be in English, and in full sentences. They cannot be abusive or personal. Please abide by our community guidelines for posting your comments.
We have migrated to a new commenting platform. If you are already a registered user of TheHindu Businessline and logged in, you may continue to engage with our articles. If you do not have an account please register and login to post comments. Users can access their older comments by logging into their accounts on Vuukle.