RTI — Right to Information Act — gives citizens the right to question any public authority, its activities, and seek information from the public domain.
Origin of RTI Act
The history of the RTI Act dates back to 1987 when Mazdoor Kisssan Shakti Sanghatan (MKSS), an activist group, protested for RTI, which led to the passing of the Freedom of Information Act in 2002. It then came to be known as the RTI Act in 2005.
According to the RTI Act 2005, “information” means any material in any form, including records, documents, memos, emails, opinions, advices, press releases, circulars, orders, logbooks, contracts, reports, papers, samples, models, data material held in any electronic form, and information relating to any private body, which can be accessed by a public authority under any other law for the time being in force.
Individuals can seek information from any government organisation across the Indian territory. The authority is under liability to respond to such request within 30 days from the date of receiving the RTI application.
“The basic object of the Right to Information Act is to empower citizens, promote transparency and accountability in the working of the Government,” the RTI website read.
Individuals can check the status of their RTI application. Here’s how:
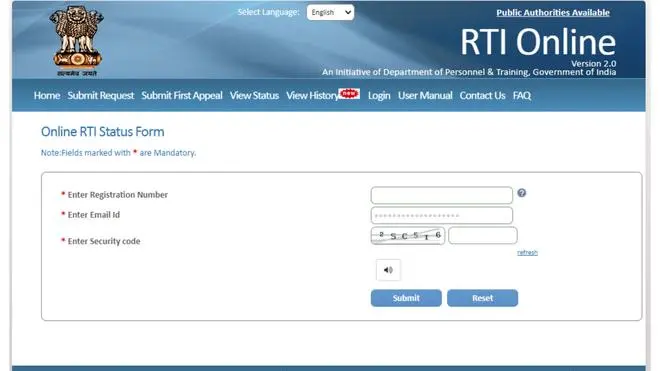
Step 1: Head to the RTI website.
Step 2: Click on ‘view status’ menu.
Step 3: Enter the registration number and email ID. Submit the request after entering the security or captcha code.









Comments
Comments have to be in English, and in full sentences. They cannot be abusive or personal. Please abide by our community guidelines for posting your comments.
We have migrated to a new commenting platform. If you are already a registered user of TheHindu Businessline and logged in, you may continue to engage with our articles. If you do not have an account please register and login to post comments. Users can access their older comments by logging into their accounts on Vuukle.